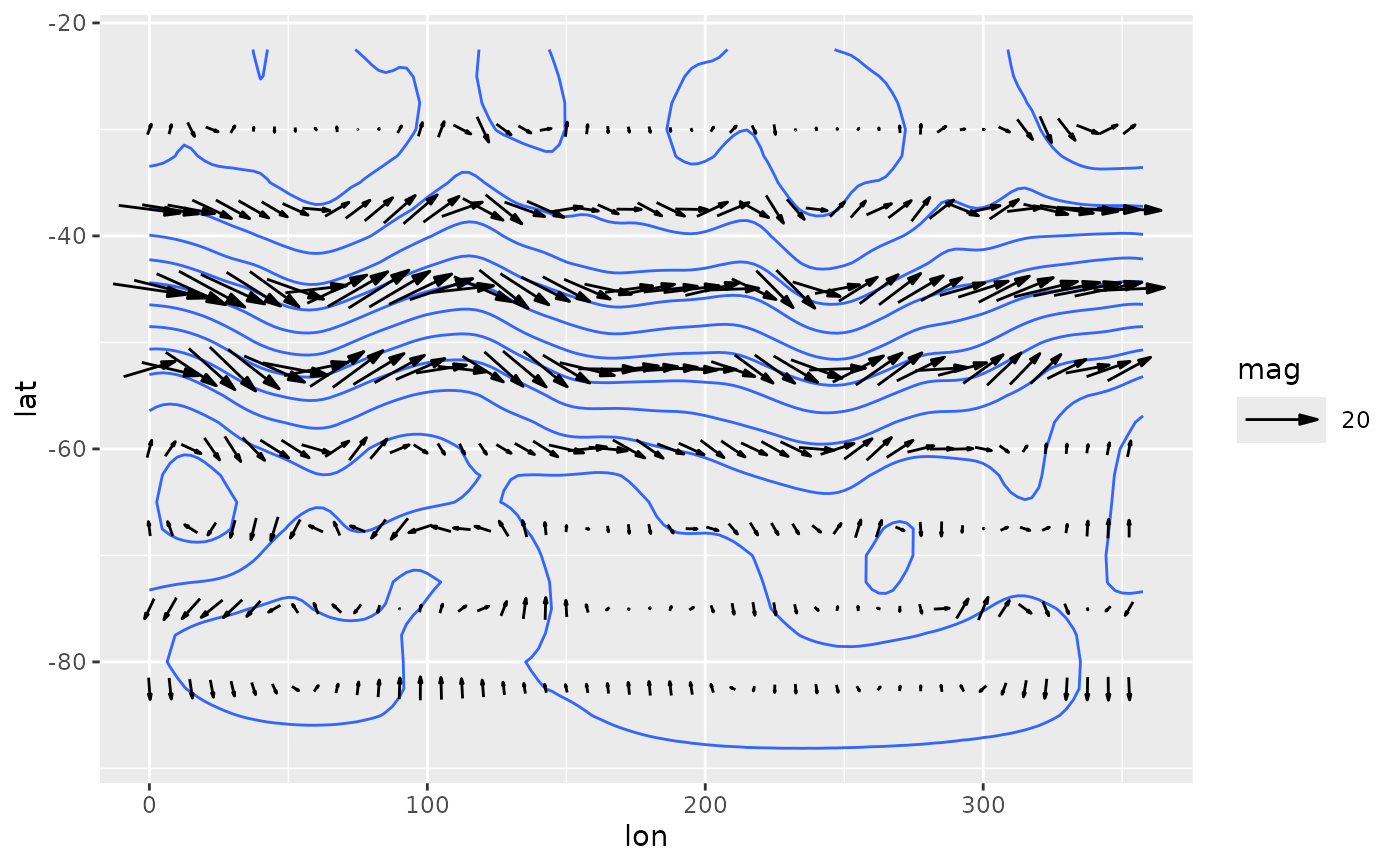
Geostrophic wind from a geopotential height field.
Details
If cyclical = "guess" (the default) the function will try to guess if lon
covers the whole globe and set cyclical conditions accordingly. For more
predictable results, set the boundary condition explicitly.
See also
Other meteorology functions:
Derivate(),
EOF(),
WaveFlux(),
thermodynamics,
waves
Examples
data(geopotential)
geopotential <- data.table::copy(geopotential)
geopotential[date == date[1], c("u", "v") := GeostrophicWind(gh, lon, lat)]
#> Index: <date>
#> lon lat lev gh date u v
#> <num> <num> <int> <num> <Date> <num> <num>
#> 1: 0.0 -22.5 700 3163.839 1990-01-01 NA 1.08181190
#> 2: 2.5 -22.5 700 3162.516 1990-01-01 NA 0.55189199
#> 3: 5.0 -22.5 700 3162.226 1990-01-01 NA 0.06625043
#> 4: 7.5 -22.5 700 3162.323 1990-01-01 NA -0.29800162
#> 5: 10.0 -22.5 700 3163.097 1990-01-01 NA -0.75064329
#> ---
#> 290300: 347.5 -90.0 700 2671.484 1995-12-01 NA NA
#> 290301: 350.0 -90.0 700 2671.484 1995-12-01 NA NA
#> 290302: 352.5 -90.0 700 2671.484 1995-12-01 NA NA
#> 290303: 355.0 -90.0 700 2671.484 1995-12-01 NA NA
#> 290304: 357.5 -90.0 700 2671.484 1995-12-01 NA NA
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(geopotential[date == date[1]], aes(lon, lat)) +
geom_contour(aes(z = gh)) +
geom_vector(aes(dx = u, dy = v), skip = 2) +
scale_mag()